Multi-Factor Authentication is a simple but effective way to guard against cyber attacks.
As cyber attacks become more common, protecting your data will become increasingly difficult. A study from Juniper Research found that by 2023, cyber criminals are expected to steal an estimated 33 billion records.
Yes, that’s BILLION with a B.
In light of the growing number of cyber attacks, many companies are turning to multi-factor authentication (also commonly called 2FA or two-factor authentication) to enhance their cyber security.
How does multifactor authentication work? We will help explain. While we aren’t tech experts, hopefully, this article will interest you enough to reach out to your IT provider and explore a solution.
What Is Multifactor Authentication? (MFA)
Multifactor authentication adds an extra layer of security to protect against compromised passwords. When you use multifactor authentication, you must confirm your identity by providing another “factor” (e.g., a phone number or unique security code) when attempting to access corporate applications, networks and servers.
This additional login hurdle means that cyber criminals won’t easily unlock an account, even if they have the password.
MFA for Personal Use
MFA can be applied for personal use, too. You may have noticed that certain online platforms like your bank, Facebook, and other sites are requiring a second level of security to sign in to your account. This is a good thing!
Using Authenticator Apps
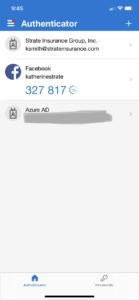
Another secure way to complete multifactor authentication is to use a time-based one-time password (TOTP). A TOTP is a temporary passcode that is generated by an authenticator app and will expire if you don’t use it after a certain period of time. With this method, users download an authenticator app, such as those available through Google or Microsoft, onto a trusted device. Those apps will then generate a TOTP, which users will manually enter to complete login.
Here are some examples using the Microsoft Authenticator app.
- Microsoft Authenticator Logo
- Sample of the Microsoft Authenticator app
Why Multifactor Authentication and Password Management Are Important
As multifactor authentication becomes more popular, some states are considering requiring it for certain industries. It’s possible that as cyber security concerns continue to grow and cyber attacks become more common, other states will follow suit.
Even if it’s not legally required, ongoing password management can help prevent unauthorized attackers from compromising your organization’s password-protected information. Effective password management protects the integrity, availability and confidentiality of your passwords.
Create a Password Managment Policy
If you own a business, you should create a password policy that specifies all of the organization’s requirements related to password management. This policy should require employees to change their password on a regular basis, avoid using the same password for multiple accounts and use special characters in their password.
These tips can also be applied for personal use.
Cyber Insurance Adds Protection
Cyber Insurance can be purchased to provide protection in case your organization suffers from a cyber attack. As much as we try to protect our business, we must plan for the worst. Reach out to your Strate Insurance Group team if you want to learn more about Cyber Liability Insurance.